Where the techniques of Maths
are explained in simple terms.
Functions - Linear models - gradient, distance and midpoint.
Test Yourself 1.
- Algebra & Number
- Calculus
- Financial Maths
- Functions & Quadratics
- Geometry
- Measurement
- Networks & Graphs
- Probability & Statistics
- Trigonometry
- Maths & beyond
- Index
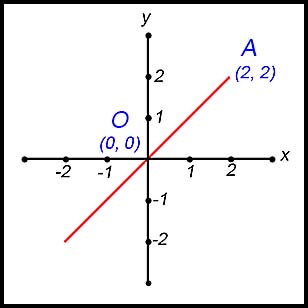
| Given diagrams. |
Answer.(iii) Gradient = 1 (iv) Length = 2√2 (v) Midpoint is (1, 1). |
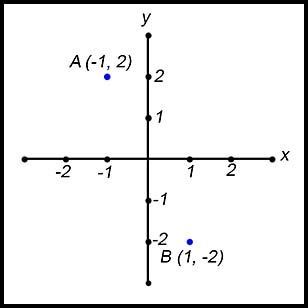
2. Using the points A (-1, 2) and B (1, -2) in the above diagram: Answer.(iii) Gradient = 2 (iv) Length = 2√5 (v) Midpoint is (0, 0). |
|
| Drawing your own diagram. | 3. Plot the points P (-3, 5) and Q (5, -2) on a set of axes.
Answer.(iii) Gradient = -7/8 (iv) Length = 10.6 (v) Midpoint is (1, 2/3). |
| 4. Plot the points M (-5, -8) and N (10, 16) on a set of axes.
By marking in the appropriate distance(s):
|
|
| 5. Plot the points A (-2, 1) and B (3, 1) on a set of axes.
By marking in the appropriate distance(s): Answer.(i) Gradient = 0 (ii) Length = 5 (iii) Midpoint is (0.5, 1). |
|
6. The points are C (-1, 3) and D (-1, -2).
Answer.(iii) Gradient cannot be defined as the line is vertical. (ii) Length = 5 (v) Midpoint is (-1, 0.5). |
|
| Miscellaneous | 7. A (-1, -2) and B (7, y) are two points on the Cartesian plane.
The gradient of the line AB is 2. Find the value of y. Answer.y = 14. |
8. P (1, y) and Q (5, 1) are two points on the Cartesian plane. The gradient of the line PQ is -2.5. Find the value of y. Answer.y = 11. |
|
| 9. The point L has coordinates (4, 3). The point M has coordinates (-6, -y).
The distance LM between the points is 5√5. What are the two possible points for M? Explain why there are two possible answers and indicate the difference in the respective gradients for LM. Answer.The points are (-6, -2) and (-6, 8). |
|
| 10. F (-3, 4) and G (a, b) are two points. The midpoint along the line joining these two points has coordinates (2, -4).
Find the values of a and b. Answer.(a, b) is (7, -12). |